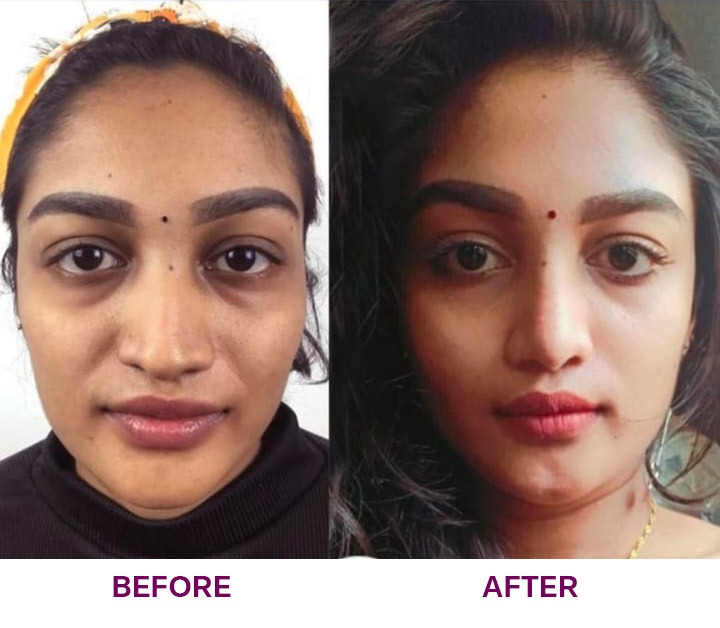
The Regional Lymph Node (N) classification is vital in assessing the extent of cancer’s spread to the lymph nodes, a crucial aspect of oral cancer staging for effective treatment strategies in the best oral cancer treatment in India.
NX: Cannot be assessed: Insufficient information to evaluate regional lymph nodes.
N0:No regional lymph node metastasis: No spread to nearby lymph nodes.
N1:Metastasis in a single ipsilateral lymph node, 3 cm or less in the greatest dimension.
N2:Metastasis with characteristics as detailed below:
N2a: Single ipsilateral lymph node, more than 3 cm but not more than 6 cm in greatest dimension.
N2b: Multiple ipsilateral lymph nodes, none more than 6 cm in greatest dimension.
N2c: Bilateral or contralateral lymph nodes, none more than 6 cm in greatest dimension.
N3:Metastasis in a lymph node more than 6 cm in greatest dimension, requiring advanced mouth cancer treatment.
Distant Metastasis (M) Classification
The Distant Metastasis (M) classification identifies whether the cancer has spread beyond regional lymph nodes to distant parts of the body, a key factor in determining the severity and prognosis of the disease, ensuring that the best oral cancer treatment in India is selected.
MX: Distant metastasis cannot be assessed: Lack of sufficient information to evaluate distant spread.
M0: No distant metastasis: No evidence of cancer spread to distant organs, indicating the importance of timely intervention and best oral cancer treatment in India for effective management.
Clinical Stages (T + N + M)
The combination of Primary Tumor (T), Regional Lymph Node (N), and Distant Metastasis (M) classifications defines the clinical stage of oral cancer, guiding personalized treatment plans and ensuring optimal outcomes for patients seeking the best oral cancer treatment in India.