Post and Core – Introduction
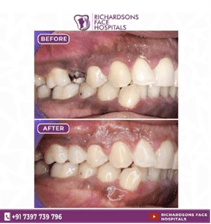
Preserving the natural tooth is always preferred over extraction and rehabilitation with artificial teeth. If the tooth is damaged, we can perform a root canal and then place a cap/crown. When the tooth is grossly decayed or broken because of the caries or trauma, or multiple times fillings, there will not be enough tooth support to hold the crown. So even after placing the crown, the tooth may be weak and the tooth will break. In such cases, it is advised to do the post and core after the root canal, and a crown is indicated over that. The post and core will act as the basement to the tooth structure, over which the core functions as the building that restores the tooth.
WHAT IS POST AND CORE?
POST:
Post is a rod-like structure material made up of fiber, metal, or ceramic, which gives the anchorage to the tooth structure with the tooth restoration, which can hold the crown. It should be placed inside the root canal space after doing the root canal treatment.
CORE:
Core is either the composite material or the dental alloy material, which should be placed around the post to compensate for the damaged tooth structure, providing the strength and stability to the crown. The core material can be either composite, glass ionomer, reinforced glass ionomer, dental amalgam, or dental alloy.
INDICATIONS OF POST AND CORE:
- More than 50 % crown structure was lost due to caries.
- Badly broken due to the trauma
- Front teeth for strength and aesthetic
- As a support for full coverage crowns
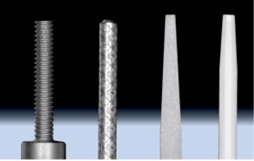
TYPES OF POST:
- Fiber post
- Metal post
- Ceramic post
- Custom-made post
- Prefabricated post
FIBER POST:
- It is made up of fiberglass or carbon fiber
- Tooth colored
- Indicated for anterior teeth because of its esthetics
- Less risk of root fracture

METAL POST:
- It is made up of stainless steel.
- Stronger when compared to the fiber post.
- Less esthetics when compared to the fiber post because of the metal
CERAMIC POST:
- Costlier when compared to other materials.
- Brittle when compared to the fiber post.
- Highly bio-compatible
- Highly aesthetic

CUSTOM-MADE POST:
- A wax pattern should be made for the tooth and the metal post can be fabricated in the lab, and it can be directly inserted into the tooth.
- The main advantage is that it fits precisely as it is customized.
- The disadvantage is that it requires two appointments.
PREFABRICATED POST:
- They are the ready-made posts which are different in size.
- They can be directly inserted into the tooth.
- The advantage is that it needs less chair-side time and can be done in one appointment.

ADVANTAGES OF POST AND CORE:
- Reduces the risk of tooth fracture by distributing the occlusal forces evenly
- Improves the function of the tooth
- To provide support to the crown
DISADVANTAGES OF POST AND CORE:
- More expensive than normal crowns
- Not indicated for severely decayed tooth structure
- It can cause a root fracture if not placed properly
- Not indicated for short root tooth
CONTRAINDICATIONS FOR POST AND CORE:
- Tooth with periapical lesion
- Tooth with a heavy occlusal load
- Patient with the habit of Bruxism
- Poor crown-to-root ratio
- Tooth with a curved root
PROCEDURE FOR POST AND CORE:
1] ROOT CANAL TREATMENT:
- The tooth that needs to have a post and crown should be root canal treated.
- The GPs that are inserted should be in tight contact with the root, and there should not be any space between the GP material and the root surface.
- Leave at least 2-3 days to check for any pain or any other symptoms
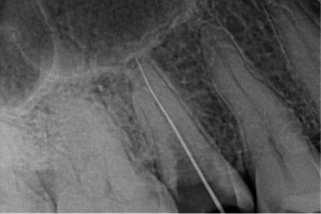
2] PREPARATION FOR THE POST:
- A small portion of the gutta-percha material should be removed from the coronal surface.
- The obturation should be proper, so that it does not come while during the post space preparation.
- The canal should be enlarged so that the post fits well.
- The canal enlargement can be done using the Peeso reamers.
- Any undercuts in the path should be removed while taking the wax pattern for the custom-made metal post.
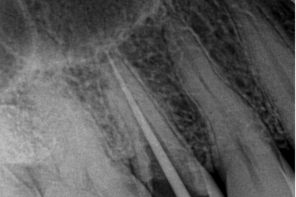
3] POST SELECTION:
- Post selection is a very important step for the longevity of the tooth.
- Anterior teeth prefer the fiber post or ceramic post.
- If all the walls of the tooth are broken, the metal post is recommended.
- Fiber posts also differ in size. Depending on the tooth size and the root length, the post size can be chosen.
4] POST CEMENTATION:
The post can be cemented inside the tooth using the luting cement
5] CORE BUILD-UP:
- Composite material can be used as the core-up material, which can be built around the post.
- The core build-up will act as the base for the crown, and it replaces the lost tooth structure.
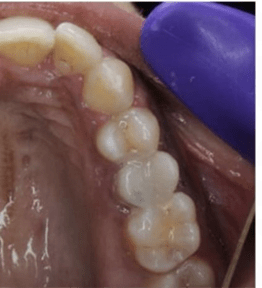
6] CROWN CEMENTATION:
All ceramic, Zirconia, or the PFM crown can be cemented as the final crown over the core build-up, so that it increases the longevity of the tooth.
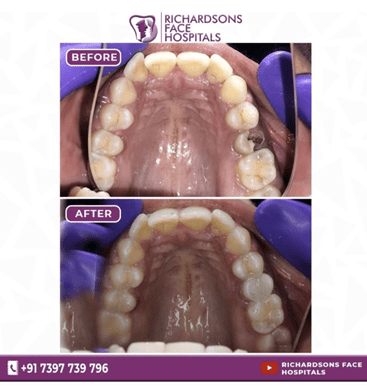
DOES THIS TOOTH REALLY NEED A CROWN?
- For all the metal post cases, the tooth needs a crown, especially for the front teeth.
- A heavy occlusal bearing tooth needs a crown.
- Shorter post needs a crown.
POST OPERATIVE CARE:
- Regular dental checkups, once in six months, are advisable.
- Oral hygiene should be maintained properly
- Biting hard objects using that tooth should be avoided to increase the longevity of the tooth structure.
LIMITATIONS OF POST AND CORE:
- It can cause a root fracture if not done properly.
- The tooth should have enough root length.
- The prognosis is poor if the tooth structure is grossly damaged.
- Not indicated for pa eriodontally compromised tooth.
- Very technique sensitive
- If not done properly, it can lead to crown failure.
- A tooth with wide canals has less post retention.
CONCLUSION:
It’s always advisable to preserve the natural tooth rather than extracting it. With adequate knowledge and hand skills, the badly damaged tooth can also be saved.